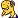

Cumulonimbus Clouds
Cumulonimbus clouds are much larger and more vertically developed than cumulus clouds which form in a more stable atmosphere. They can exist as individual towers or form a line of towers called a squall line often present at cold fronts. Underneath they are dark and menacing. At a distance they rise up like huge white mountains when the Sun shines on them, and are commonly topped with anvil-shaped heads. Fuelled by vigorous convection of air in an unstable atmosphere the tops of cumulonimbus clouds can easily reach 12 km or higher. Lower levels of cumulonimbus clouds consist mostly of water droplets while at higher elevations, where temperatures are well below 0°C, ice crystals dominate.
During the formation of the larger cumulonimbus, condensation droplets are carried up and down several times within the convection currents inside the cloud before being released, coalescing to form raindrops. The more vigorous the thermal currents inside the cloud, the larger the raindrops which form. Light showers can fall form modest-sized "cauliflower" clouds whilst the larger cumulonimbus clouds can produce heavy downpours. The largest cumulonimbus clouds of all are found in thunderstorms. In these clouds up-currents are so severe that splitting of raindrops and ice crystals can occur before re-coalescing and falling to the ground. It is believed that this may contribute to the build up of electric charge and the occurrence of lightning.
 | Cumulonimbus cloud |
Websites
Other topics
• Cumulonimbus
• WW2010
• PSC Weather Center
• Weather Terms
• Introduction to Weather
• Anticyclones
• Beaufort Scale
• Cirrus Clouds
• Clouds
• Cold Fronts
• Condensation
• Convection
• Cooling Air
• Cumulonimbus Clouds
• Cumulus Clouds
• Depressions
• Dew
• Dew Point
• Energy
• Evaporation
• Fog
• Forecasting
• Fronts
• Frost
• Humidity
• Hurricanes
• Isobars
• Measuring Weather
• Meteorology
• Monsoons
• Movement of Air
• Occluded Fronts
• Precipitation
• Pressure
• Sea Breeze
• Stability of Air
• Stratus Clouds
• Sunshine
• Synoptic Charts
• Temperature
• Thunderstorms
• Tornadoes
• Uplift of Air
• Warm Fronts
• Water Cycle
• Weather Symbols
• Wind
 Print Topic
Print Topic